With a long-range wireless network, you can track your cargo in real-time and improve your yard management systems. Long-range wireless networks enable you to reduce your reliance on GPS by providing batteries that last longer and connections that are more reliable.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Long-range wireless networks enable seamless connectivity across vast industrial and urban areas.
- Logistics benefit through real-time cargo tracking, yard management, and efficient asset monitoring.
- Manufacturing uses these networks for predictive maintenance and environmental condition monitoring.
- Remote infrastructure, like wind farms and railways, is efficiently supervised using wireless networks.

It’s more than obvious that wireless networks have become an integral part of our lives, because, without them, people and companies from different industries wouldn’t be capable of accessing the internet and having a seamless connection wirelessly.
These days, practically every household (or at least the vast majority) utilizes Wi-Fi, plus a lot of businesses of different sorts are heavily reliant on wireless networks. Technologies, such as Sigfox, LoRaWAN, and many others, play a crucial role in modern industrial operations.
All of these networks have the ability to address numerous connectivity gaps without using massive infrastructure, and that’s what makes them so useful and powerful. What used to seem impossible, today has become a normality because of them, and this article will further dive into this topic to show how different industries make use of these networks.
According to a report issued by MarketsandMarkets, the global wireless connectivity market is expected to be $199.3 billion by 2027 as a result of the growing IoT, smart infrastructure, and remote industrial applications.
Long-range wireless networks represent a promising new aspect of communications technology that enables devices to connect wirelessly and seamlessly across long distances without needing to follow the electrical path of wires. These networks are most applicable to industries that require multiple continuous monitoring, data collection/modification, or automation applications across a longer physical distance.
In this article, I will highlight the industries that are utilizing these networks, the benefits of the networks intuitively, and their capacity to help the future development of the industry.
Logistics & Supply Chain
Certainly, one of the most significant changes in this regard can be found in logistics. By virtue of the long-range wireless networks, today, firms from this industry can conveniently monitor their assets as they move, regardless of their location.
- Cargo monitoring – Shipping containers, valuable items, and many other things can be fitted with trackers that are designed to provide recipients with the real-time location and state of their goods.
- Yard management – In rail yards, operators can leverage wireless sensors to immediately locate equipment and, concurrently, drastically reduce the risks of any delays.
Although there are still some businesses that use GPS, it’s safe to say that long-range is slowly replacing them because they are way more versatile and efficient. Plus, unlike GPS, they can employ a single battery for a very long period of time.
Industrial Automation & Smart Manufacturing
Anyone working in factories knows that downtime often leads to extremely costly losses. That’s precisely why wireless network connoisseurs at https://www.concept13.co.uk/ want to accentuate the fact of how critical it is to have reliable data. Luckily, long-range wireless networks perfectly complement wired systems by connecting assets that aren’t easy to reach with cables.
- Environmental tracking – These devices can monitor temperature, humidity, and air quality in various product productions environments.
- Predictive maintenance – Machines that come with temperature and vibration sensors can report on time on early signs of wear, preventing massive damage that may halt production.
Since these networks are able to support numerous devices, it’s safe to say that they are perfect for large-scale deployments. Below, you can see the major benefits of long-range wireless networks.
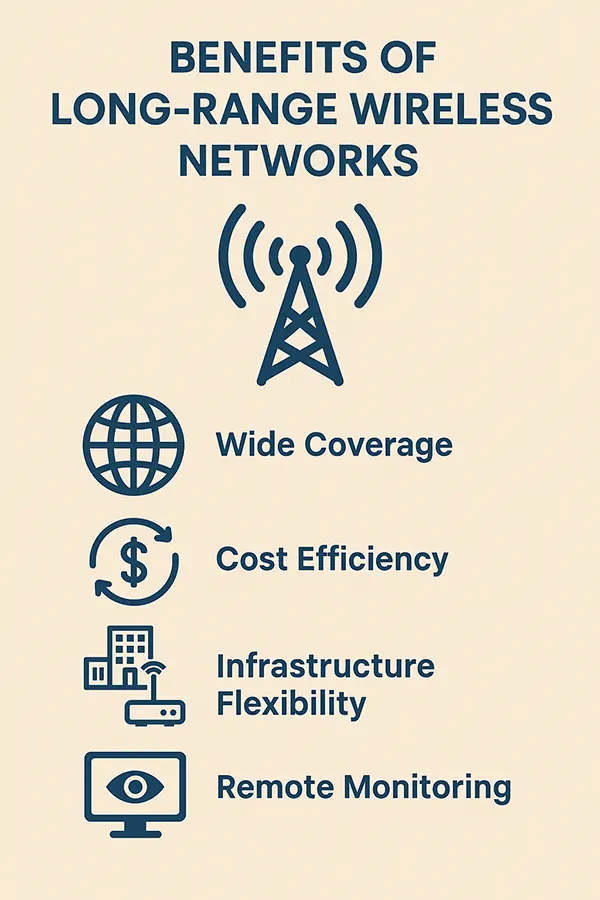
Remote Infrastructure Supervising
In different industries, such as transportation, energy, and others, assets are frequently spread over areas that are difficult to reach. In the past, overseeing these areas demanded costly wired systems or time-consuming manual inspections.
Thankfully, that’s no longer necessary, and it’s all due to long-range wireless networks. They have improved these processes significantly, allowing for reliable and continuous remote monitoring. For instance, in a wind farm, every single turbine can easily send weather readings, performance metrics, and other important pieces of information to a central system.
Additionally, railway operators make use of similar systems to supervise track conditions and detect potential problems on time before they cause bigger issues or delays.
Urban Environments
Today, you can often see various urban environments that are utilizing long-range wireless networks, practically including them in their smart city infrastructure. Streetlights are now able to alert whenever maintenance is necessary, emergency services can make use of connected fire hydrants that are specifically intended to report pressure status, and flood sensors can alert when there’s an issue with the water levels.
Furthermore, lots of municipalities use air quality monitoring networks that encompass entire districts, providing both the public and authorities with real-time data. These advancements offer numerous benefits, enhancing city management while fostering greater reliability and trust among the public.
Agriculture

Until recently, various connectivity challenges had delayed the widespread adoption of precision farming practices. Nowadays, thanks to the long-range networks, farmers can efficiently supervise soil moisture, control irrigation systems from any location, and monitor livestock.
For example, cattle that are equipped with trackers can be located in a flash across open fields. In forestry, networks can utilize fire detection sensors, connect weather stations, and employ wildlife tracking systems in literally any area without needing to have a human presence.
Embracing these networks marked a groundbreaking shift, elevating the efficiency of companies across multiple industries to unprecedented levels. As industries continue to embrace digitalization, it’s safe to say that the demand for wide-area connectivity will most definitely grow in the future.





