Identifying the source language ensures accurate translation of technical terms and nuances, preventing misunderstanding and maintaining original meaning.
When working with international clients, there are different challenges that a company encounters. Especially, these are often related to dealing with invoices in different languages, making the process more complex and time-consuming.
Even for the accountants and bookkeepers, this issue adds another challenging factor, such as financial reporting, compliance checks, and expense tracking. In fact, about 1–2% of errors that a business experiences on all invoices are processed manually [source: Parseur].
The data highlights that invoice processing is already complicated, and language barriers can make it even more tedious. So, what could be the solution for this particular scenario?
Well, the solution lies in the problem. Thereby, this article will help you explain the importance of the integration of foreign languages and strategic techniques to handle the accounting workflow.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Businesses are outsourcing materials from different countries, which results in an increasing number of foreign language invoices.
- First, identify the source language to detect technical terms and industry-specific phrases.
- Misreading important terms, different formatting rules, and misinterpretation of words are some challenges while processing non-English invoices.
- AI tools can help in instant translation of invoices, avoiding human errors.
- After using an AI tool for translation, give it human oversight to detect possible mistakes.
- While filing taxes, auditing documents, and sending them for a legal review, an accounting firm should hire a professional translator.
- After a successful invoice translation, make a folder, use a multilingual record tool, and add metadata to effectively organize and store translated invoices.
Why Foreign Language Invoices Are Increasingly Common
The foremost reason behind foreign language invoices becoming increasingly common is due to the explosive growth in global marketing. Businesses are sourcing materials, manufacturing components, and offering services globally. All of these processes may involve supplier bills for different products and services.
In another case, COVID–19 may significantly accelerate the adoption of remote work, resulting in companies hiring higher talent from different corners of the world. This rise of remote work included cross-border transactions and international e-commerce, along with language diversity.
First Step: Identify The Source Language
As you have got the answer in the previous section, now it’s time to figure out the source language. Yes, it might sound obvious, but it is necessary to detect in case you got two different invoices: one in Germany and another in Japan.
In fact, these invoices can contain technical terms, unfamiliar abbreviations, or industry-specific phrases, which can make it even difficult to identify the language. Some platforms are available to auto-detect language, while you can use a free language detection tool as well.
Challenges Of Processing Non-English Invoices
The issues associated with foreign language invoices are not restricted to translation only. Beyond that, it can create scenarios of different types of scenarios mentioned below:
- Misreading a tax code, line point, or payment term which would probably result in incorrect reporting or compliance failures.
- Different countries might have distinctive formatting rules.
- A country may have the same word as you, but with an entirely different context.
As a result, these things would create a change of errors slipping into your records, especially when handling multiple language vendor accounts at the same time.
Using AI Translation For Fast Internal Review
Do you know that not all invoices in other languages need to be fully translated by a professional? How so possible? If your team frequently handles international paperwork, using AI in the invoice review process can help save time while gathering all the details.
For regular documentation or instant internal use, AI translation tools can offer a fast and cost-effective way of understanding the context. This section will particularly focus on using AI appropriately and explain how to make sure the translated content is accurate and executable.
When AI Translation Is Appropriate
Determining if the AI translation is appropriate or not can be done through a simple observation. When the invoice is used for internal operations only, such as classifying expenses, verifying payment amounts, or matching vendor records, AI translation can work well.
It is specifically useful for recurring invoices or low-risk transactions that have a predictable format. Individuals can also rely on AI for invoices with a clear structure and simple language. In these cases, the main goal is speed and general understanding rather than legal precision.
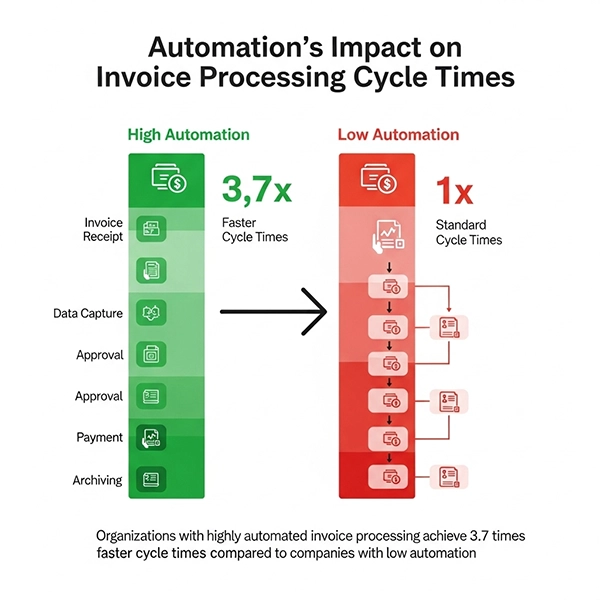
INTERESTING FACT
Organizations with highly automated in vice processing achieve 3.7 times faster cycle times as compared to companies with low automation.
Tips For Reviewing AI-Translated Invoices
AI-based inverse translation and process can definitely boost efficiency, but beyond that, human oversight is still important to ensure accuracy and prevent errors for sending to further financing AI tools. Learn some key tips for reviewing AI-translated invoices:
- Always check everything twice, including the amount, currency totals, and taxes.
- Confirm invoice due and payment term dates.
- Ensure that vendors/clients’ names, addresses, and bank details are written correctly.
- Be aware of small details like decimal shift or missing zeros.
- Look if there are any misinterpretations of industry Jargon or abbreviations.
Implementing these tips during analysis enables the whole team to catch errors and prevent major losses.
Common Errors To Watch For
Apart from general review tips, one should be particularly vigilant for these common errors that occur during AI translation.
- Numeric errors that include transport numbers or decimals.
- Contextual misinterpretation of industry-specific terms.
- Formatting issues while going through a complex layout lead to incorrect data extraction.
- Sometimes parts of invoices might be entirely overlooked, resulting in incomplete data.
When A Professional Translation Is Required
Sometimes you require more than air translation for operational management and procedures. It should be done more accurately in case of tax filing, audit documentation, or legal review. If you are already looking for skilled training, you can seek assistance from a professional translator who specializes in financing.
An expert guide will help you go through all the terms, formats, and legal references that are needed when proceeding with clients.
Legal And Audit-Sensitive Documents
Now comes the invoices that support financial audit regulatory compliance or text filing. These documents may contain legal clauses, financial disclosure, or jurisdiction-specific terms, which, of course, must be translated more precisely.
Additionally, documents are vital for understanding obligations or liabilities, and depending on AI software for these types of context may increase the risk of misinterpretation.
Industry-Specific Compliance Needs
Industry specific compliance refers to industries having strict documentation rules for the translation process. Such industries include finance, health care and some of the government sectors, especially for billing regulatory statements and tax codes.
In this case, taking help from an expert translator who understands industry context would be a great idea. Since any translation in the specific sectors may lead to compliance issues or approval delays.
Benefits Of Certified Translations
Want to know the benefits of having certified translations? Here are the key advantages of choosing certified translations in the invoice process:
- Certified translation ensures accuracy and completeness.
- This adds a layer of accountability required for official submissions.
- Financial reviews and other official examinations can be done easily.
- The communication process becomes smoother.
- It reduces the risk of a misinterpretation, rejection of documents, or financial penalties due to translation inaccuracy.
- Through these, businesses can comply with the legal and regulatory requirements in foreign markets.
How To Organize And Store Translated Invoices
After translating the invoice data, professionals need to classify it for easy access and long-term compliance. In this section, we will specifically talk about organizing and storing the translated invoices.
Folder Structure And Naming Conventions
Based on region vendors or accounting periods, create a consistent folder structure. You can group invoices using the year, and then using the language or country. For example, “Willings_2924_Japan” immediately expresses the content and its origin without opening it. This makes it more convenient to track documentation and retrieve particular records during tax season or audits.
Tools For Managing Multilingual Records
Plenty of tools are available in multiple languages to streamline the invoice management process. Starting with an accounting platform such as Xero and QuickBooks that allows attaching a translated version of documents straight into transactions.
On the other hand, shared drives or document management systems can also be used with multilingual search features. The overall process assists in keeping records in one place and is easy to search.
Metadata And Tagging Tips
At last, incorporating metadata into translated invoices can categorize the important documents. Language, currency, vendor nation, and translation techniques are a few other features that may be added to the file. Also, during audits or reviews, using enhanced visibility and initiating reporting.
Final Tips For Cross-Border Invoice Management
As cross-border trades grow more common, establishing a language-oriented workflow in accounting firms becomes more essential.
Processing foreign language invoices is not a piece of cake. However, when you have the correct AI tools, solid documentation organization, and a human translation when required, every compliance can be efficient and smooth.
- Why Foreign Language Invoices Are Increasingly Common
- First Step: Identify The Source Language
- Challenges Of Processing Non-English Invoices
- Using AI Translation For Fast Internal Review
- When A Professional Translation Is Required
- How To Organize And Store Translated Invoices
- Final Tips For Cross-Border Invoice Management




