Schedule C tax form is an IRS form used by sole proprietorships to file business expenses and income to analyze the amount of tax owed.
“If you’re your own boss, then the Schedule C tax form is your business financial diary.”
Yes, you read it right! The 1040 Schedule C form is your financial diary that records all business expenses and income for the tax year. As a self-employed individual, you are subject to file this form in the United States.
But how do you report detailed information on IRS Schedule C?
Don’t fret about it — I have covered everything from what it is to how to file this form, along with the Schedule C instructions.
So, stay till the end to learn how to keep accurate records of your business expenses and income.
What is Schedule C Tax Form?

Schedule C tax form is used to report the income and expenses of a sole proprietorship business to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It calculates the net profit and loss of your business, which is then reported on your personal income tax return (Form 1040).
Moreover, this form helps self-employed individuals, such as freelancers, small business owners, and consultants, to track what they make or spend per year in their business. This way, they easily determine the amount of taxes they owe at the end of the year, which helps in calculating the correct tax liability.
However, some ventures will turn into highly profitable businesses, resulting in paying more income tax. On the other hand, small business owners are struggling with the tax burden. That’s why the US government wants to reduce the tax burden during the time they are most likely to fail after analyzing the Schedule C tax form.
Who Files a Schedule C Tax Form?

Sole proprietors or self-employed individuals are allowed to file the Schedule C tax form. While corporate employees, partnerships, or multi-member LLCs are not required to submit this form.
Here is the list of people who need to file a 1040 Schedule C:
- Sole Proprietors
A business structure with no legal distinction between the owner and the profession.
- Freelancers
Individuals who offer their services to the public are considered self-employed.
- Gig Economy Workers
People who earn income by providing services on demand. For example, on-demand drivers for ride-share.
- Single-Member LLC Owners
A person who owns a single limited liability company, meaning the business profits and losses are reported on the owner’s personal tax return.
- Qualified Joint Ventures (Spouses only)
A business owned by a married couple is allowed to file a Schedule C tax form, instead of a partnership return.
After acquiring knowledge on “What is Schedule C tax form?” and “Who is eligible for it,” you need to dig deeper into the next section to learn Schedule C instructions.
Instructions for Filing a Schedule C
To fill out your Schedule C tax form, you have to gather all essential information related to your business’s income and expenses.
Here is the following information you need to fill in this Schedule C form:
- Your name and business name
- Address
- Accounting method (cash or accrual)
- Business expenses, like advertising, maintenance, equipment, and furniture.
- Business income, like revenue from sales and commissions.
- Information about Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Details about the vehicle used in your business.
- Gross receipts or sales
- Inventory records
- Social Security Number (SSN)
- Product or service activity
How to File a Schedule C Tax Form?

You need to add business-related details, such as income, expenses, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), information on your vehicle, and other expenses to the 1040 Schedule C IRS form.
Here, I’ve jotted down step-by-step guidance for you to effortlessly learn how to file this tax form.
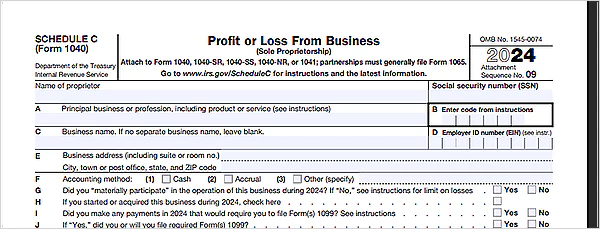
Step 1: Add Business-Related Information
Firstly, you need to fill in information, such as the proprietor’s name, business name, profession, Social Security Number(SSN), Employer Identification Number, and business address.
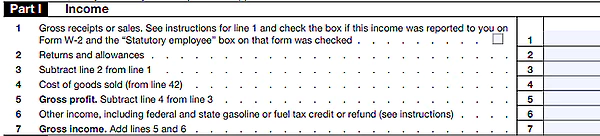
Step 2: Part I — Income
In this section, you should report all income received from gross receipts or sales, returns and allowances, and other earnings from customers, clients, or patients related to your business. It is important to note that this is the total amount of income before deducting any expenses.
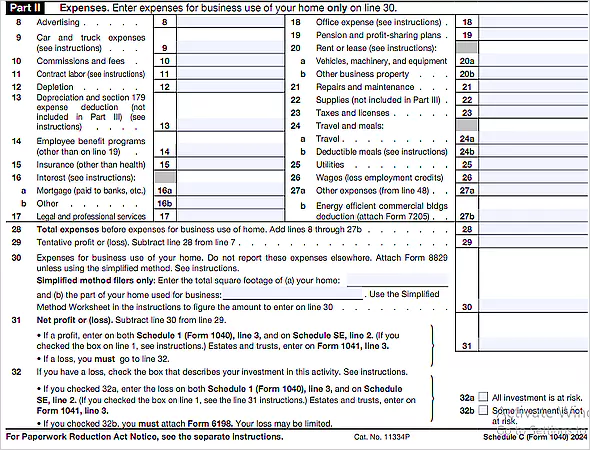
Step 3: Part II — Expenses
Now, you have to report your business expenses, such as rent, utilities, advertising, equipment, interest, insurance, travel and meals, mortgage, wages payable, and other costs. It is an integral part of a Schedule C form because it helps to calculate net profits and losses.
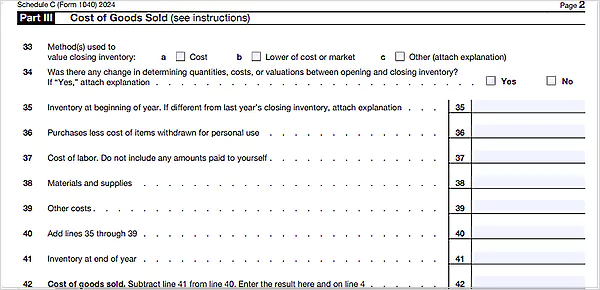
Step 4: Part III — Cost of Goods Sold
The Cost of Goods Sold section reports all direct expenses associated with making a product during the year, e.g., material or labor. It is essential to calculate COGS because it is subtracted from gross receipts to determine gross profit. Afterward, this information is used to determine net profit and loss, which is reported to your personal income tax return.
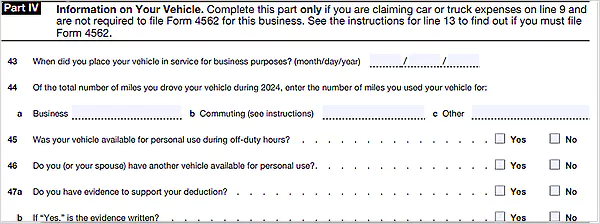
Step 5: Part IV — Information on Your Vehicle
In this section, you only fill in information related to your business-use vehicles. This includes the total miles you drove and the expenses related to your car or truck for business purposes.
Step 6: Part V — Other Expenses
At last, the “other expenses” section is for any other business expenses that aren’t reported anywhere else in the Schedule C tax form. However, it is crucial to keep accurate records and receipts for the final audit-ready form.

Schedule C Vs Schedule C-EZ: What’s the Difference?
Before 2019, sole proprietorships were required to fill Schedule C-EZ, which was a simpler version of Schedule C. However, the IRS discontinued this form and mandated the Schedule C tax form for all self-employed individuals.
Let’s see the breakdown table of Schedule C and Schedule C-EZ to know the difference between them.
| Feature | Schedule C | Schedule C-EZ |
| Current Status | Presently available for filing the profit and loss of the business. | Discontinued after the 2018 tax year. |
| Eligibility | Sole proprietorships and single-member LLCs. | Taxpayers whose business expenses $5,000 or less, and who reported a net profit. |
| Complexity | Integrate the five parts that require detailed information on business expenses and incomes. | A single page that only needs one line for most expenses. |
| Filing Process | Requires more time and detailed record-keeping. | A quicker way to report expenses with a simple format. |
The Bottom Line
With the above-mentioned information, you might get an answer to the query, “What is Schedule C tax form?”
Schedule C tax form is used to report all business income and expenses to the IRS. This report helps you analyze the amount of tax you owe during the year.
On top of that, if you find filing the Schedule C tax form a complicated task, you should opt for tax outsourcing services. Their expertise helps you to keep accurate records of profits and losses for making informed decisions.