Chargeback is a term typically used for transaction reversal that is a nightmare for any business. While there may be various reasons for which these transactions are reversed, customer disputes with the bank or the recipient’s account are typically the main reason.
To resolve the issues, banks are responsible for initiating an investigation. In case of technical difficulties, the amount is generally either reversed to the sender’s account or transferred to the recipient’s account.
This discussion is going to cover all aspects of the subject in the easiest way possible. So, read till the end. Also, learn about Payment Integration for Small Businesses by reading this article.
What is a Chargeback?
Chargeback is a business term typically used to explain transfer disputes or reversal amounts. Normally, in the case of payment through a credit card or a debit card, the issue is raised by the customer for the problem with the payment.
If this happens, the first thing to do is to reach out to the bank and report the issue. Later on, it is up to the bank to investigate, look for submissions, and take the final action. Then how is it a nightmare for businesses? Well, if the customer’s complaint is valid, the amount gets deducted from the merchant’s account and is transferred to the customer’s account.
The worst that can happen is a merchant’s uneven relationship with merchant account processors.
Types of Chargebacks
Chargebacks are not of a single type. It can be classified as:
- Criminal Fraud Chargebacks: As the name suggests, this happens in a sensitive situation when the information of the sender is somehow stolen or leaked without permission. This way, if the transaction is made, the money is charged back to the victim as soon as possible.
- Merchant Error Chargebacks: If there is any mistake from the merchant’s side, the money can be reversed if the buyer claims for it. Speaking of these mistakes, they can be either a billing mistake, an issue in delivery, or any other problem.
- Friendly Fraud Chargebacks: The biggest nightmare for businesses is when a customer returns or claims the product is faulty to get a refund. In such cases, the buyer also keeps the product with themselves, while asking for a refund from the merchant’s account.
The Impacts of Chargebacks on Businesses
Now, it has been a no-brainer that chargebacks for businesses are not for good. From a business perspective, the following are some consequences that they have to face:
- Lost Revenue: It gets really frustrating for merchants when a customer communication claims a chargeback, as it leads to cuts from the merchants’ accounts. Technical difficulties are all okay, but fraud chargebacks are a menace.
- Damaged Reputation: More chargebacks mean there is something wrong with how a business deals with its operations. Moreover, not only does it degrade their online presence in the e-commerce scene, but it also leads to negative reviews online.
- Increased Fees: Chargebacks do not come empty-handed. They bring a lot of charges and fees for the merchants that are to be deducted from their accounts (along with the reversal amount). With a combined amount of chargebacks, a business of any scale can land a significant amount.
- Operational Cost: To check whether the claim is right or not, also other functions like processing the chargebacks, etc., all make the entire process more time-consuming and expensive. Hence, it does not only make a loss for the business’s money but also the time.
- Account Restrictions: Excessive amounts of chargebacks or transaction reversals may also lead to some restrictions on the business’s accounts. These restrictions include limiting the transaction amounts, charging penalties, etc.
Best Practices for Chargeback Management
Without any doubt, maintaining a chargeback-free company is a challenge on its own. Also, recovering from such losses becomes tiring for those who work to make successful deals.
However, you still need to make your efforts and try for as low chargebacks as possible. Here’s how it is possible:
- Deploy Strong Systems for Fraud Detection: There are high chances that the customer you are dealing with might be a fraud. To keep yourself away from such situations, you must invest more on security infrastructure and integrate modern tech pieces like AI and ML.
- Clear and Transparent Policies: Largely, the reason for chargebacks is a misunderstanding between the customer and the business. To avoid such situations, build a clear policy and share it with buyers completely transparently.
- Monitor Chargebacks Metrics: While giving your efforts, it becomes necessary to keep track of the process. How well is the team performing, or where are the efforts lacking? Such information collectively makes a huge impact on the decision-making process. Hence, keep a look at those metrics and stay aware of the scene.
Understanding Chargeback Fraud And Prevention
Finally, there are some solutions to prevent such unfortunate situations that may cost a fortune on your bank account:
- Customer Verification: To prevent yourself from fraud, you must start verifying whether the user is legit or not. For that, companies use some procedures that go like”
- 3D Secure (3DS)
- Address Verification Service (AVS)
- Blacklists/Whitelists: Sorting customers into black or white lists is another idea that businesses implement. A blacklist consists of those customers that are suspicious to claim false or fraudulent chargebacks. Whereas, the whitelisted customers are completely opposite.
- Chargeback Fraud Education: In case some customers do not know about the consequences they may have to face for fraud chargebacks, it needs to be corrected.
The Role of Chargeback Insurance
Businesses insured with chargeback insurance enjoy protection from financial losses caused due to chargebacks. For a business, chargeback insurance is necessary for the following aspects:
- Financial Protection: If the chargeback happens, the insurance providers reimburse the amount with some reasonable deductions.
- Mitigate Potential Risk: If not avoided, fraud chargebacks can cost heavily on businesses. With that point of view as well, chargeback insurance is a big win.
- Peace of Mind: With trusted insurance and extensive risk mitigation capabilities, businesses can operate with a free mind, ultimately resulting in better productivity.
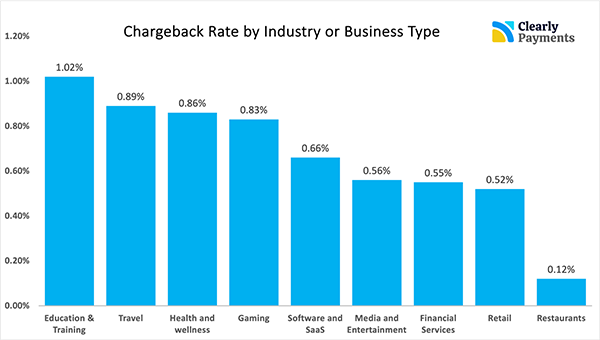
Like this, the role of chargeback insurance is pretty crucial in the industry. However, if you are wondering how often these events happen, the following graph shows the industry-segmented data on the same subject.
Resolving Chargeback Disputes
Resolution of the chargeback is a step-by-step process that involves both parties, i.e., the merchant and the customer. The following list shows how it’s done:
- Customer Initiates Dispute: If there are any problems in the transaction through a credit card or debit card, the client immediately raises its flag for a chargeback. This is where everything starts.
- Issuer Reviews Dispute: The issuer takes the responsibility to investigate if everything seems legit, and if the cardholder is also legit or not.
- Merchant Notified: The merchant gets notified of the chargeback claim. All the necessary details and the buyer’s identity are shared with the merchant.
- Merchant Responds: The merchant gets a limited time period to respond to the claim. Whether it’s about providing evidence or simply approving the claim, anything has to be done within a limited time.
- Issuer Decides: On receiving replies from both parties, the issuer gives its take on whether the chargeback needs to be processed or not.
Final Words
In easy words, chargeback to just the transaction reversal that a buyer claims when there is an issue with the payment through a card. Chargeback is a nightmare for the merchant as it is considered as a loss to the business plus it also charges an amount in exchange. This article covered all the necessary details about it and how this issue is resolved.







