A multiple step income statement refers to the comprehensive financial report that contains detailed information about the operating and non-operating items that assist in determining precise net income and profit figures.
A multi step income statement is the financial report that a business prepares to gather an in-depth understanding of its profits, revenue, costs, and expenses.
While large-scale firms often utilize multiple step income statements, small businesses can also benefit from these financial reports to check the profits generated from the core business operations.
While multi step income statements might seem complex, you can easily understand through our detailed article that covers their meaning, importance, formula, and comparison with a single step income statement.
What Is a Multi Step Income Statement?

A multi-step income statement is a financial report that businesses prepare to gain an in-depth understanding of profits, revenue, costs, and expenses.
However, it is different from the single step income statement, as a multiple-step income statement reports multiple levels of income and profitability, giving a more comprehensive insight into the total revenue and expenses.
Since multi step income statements categorise operating and non-operating accounts effectively, it allows firms to have a precise value of total net income. In addition, a multiple step income statement has separate sections for all the essential aspects, including costs affecting business activities.
Why Is a Multi Step Income Statement Important?

If you are wondering why a multi step income statement is more important than a single step income statement, it is due to the substantial information required for the firm’s actual profitability and core operations.
While a single step simple income statement deducts total expenses from revenue, a multiple step income statement equips firms with the potential of segregating operating heads from the non-operating ones for net income.
In addition, the primary benefits of multi-step income statements include:
- Profit analysis: Firms can calculate the profit before total expenses using the multi step income statement equation, along with better cost evaluation for comprehensive profit analysis.
- Business performance evaluation: With the detailed information on gross profit, operating, and net income, organisations can empower their business performance and build strategies that foster revenue growth.
- Financial decision-making: Through optimal insights into financial health, businesses can develop substantial financial planning along with improved decision-making by mitigating inefficient expenses.
- Core operating and non-operating items: If businesses need to identify the weak areas and determine precise net income, using the multi-level income statement formula will help in separating core operating and non-operating accounts.
Structure of a Multi-Step Income Statement

Since multiple step income statement segregates operating revenue from non-operating items, it is crucial to determine gross profit, operating, and non-operating income to calculate net income. Subsequently, the structure of a multi step income statement includes:
Revenue
The preparation of a multiple step income statement starts with determining the revenue that the business has generated over the financial period. In easy words, you can determine this as the firm’s actual income derived from core sales.
Furthermore, you have to deduct the sales returns and discounts from sales numbers to gather precise figures of actual income.
The income statement formula for revenue is:
Sales Revenue – (Sales discounts + returns)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The Cost of Goods Sold or COGS refers to the actual value of the goods manufactured or bought for further sales to generate revenue.
Subsequently, COGS is mentioned after the revenue in the multi-step income statement equation that determines the expenses made by the firm on acquiring assets before calculating operating expenses.
The income statement formula for Cost of Goods Sold is:
COGS = (Initial Inventory + Purchase Of Goods) – Ending Inventory
Gross Profit
The gross profit comes after the calculation of revenue and COGS, as you now have to deduct the cost of goods sold from the sales revenue to determine the profit made by the firm in the financial period.
Subsequently, this allows firms to gain insights into financial performance for optimal utilisation of resources and enhancing revenue growth.
The income statement formula for Gross Profit is:
Gross Profit = Sales Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Operating Expenses
While COGS represents the value spent on acquiring goods for further sale, the operating expenses are the daily operational costs that are incurred during day-to-day operations.
From salaries of employees to rent and utility bills, along with advertising, marketing, delivery, and research & development costs, everything comes under operating expenses and is calculated to achieve the precise figures of net income.
The income statement formula for Operating Expenses is:
Operating Expenses = Selling Expenses + Administrative Expenses
Operating Income
Operating income gives information about true profitability, as you will now have to deduct the operating expenses from gross profit to know the details about operating income.
Besides this, operating income is also EBIT (earnings before interest & taxes), as it doesn’t include taxes and accounts for the profit after deducting money spent on daily operations.
The income statement formula for Operating Income is:
Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Non-Operating Items
Whether your firm has earned interest from investments, rents, sale of long-term assets, or your firm has paid the liability of interest and taxes, these are all calculated under non-operating accounts.
Since it focuses on revenue or expenditure not incurred during core business activities, multi step income statements allow firms to gain significant insights into actual profitability from core operations.
The income statement formula for Non-Operating Items is:
Non-Operating Accounts = (Non-Operating Revenues & Interests) – (Non-Operating Losses, Interests, & Taxes)
Net Income
With the detailed insights on every aspect of expenditure and revenue, your firm can efficiently calculate net income by adding non-operating items to operating income or profit.
In addition, this net income provides details of the net profitability that your business has generated, which reveals financial performance during a specific financial period.
The income statement formula for Net Income is:
Net Income = Operating Income + (Non-operating Income – Non-operating Expenses)
Multi-Step Income Statement Format
Since a multiple-step income statement reports multiple levels of profit through the effective calculation of revenue and expenditure, you will need to analyse your reporting period before its calculation.
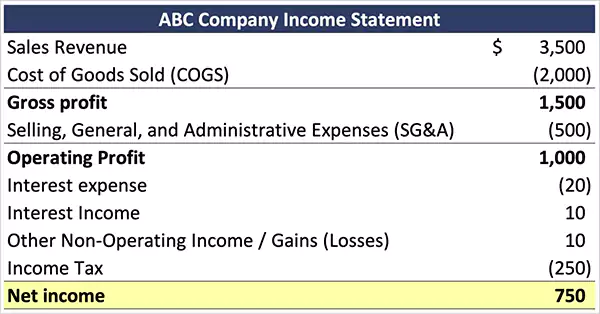
Besides this, the multi step income statements format must include the following points:
- Start by creating a header called Income Statement that must contain the end date of the accounting period, along with the date and your firm’s name.
- Prepare sections for Total Revenue from Sales and Cost of Goods Sold.
- Calculate and mention Gross Profit by deducting COGS from Revenue.
- Mention items in Operating Expenses and calculate the subtotal.
- Calculate Operating Income and mention it in the next section.
- List all the accounts of non-operating revenues and non-operating expenses, losses, and taxes.
- Lastly, calculate Net Income by deducting Non-operating accounts from Operating Income.
Example of a Multi-Step Income Statement

If you are guessing what an income statement looks like, we have listed a multi step income statement example with detailed steps covering each essential aspect. Refer to the multistep income statement example below:
- Have a look at the multi step income statement of Robert Solutions for the 2025 financial year, where they generated a net income of $4090 and gross profit of $5100.
Income Statement of Robert Solutions for the year ending in 2025 (in $) Sales
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses
Selling Expenses
Advertising Expenses: 100
Sales Commission: 300
Administrative Expenses
Supply Expense: 60
Rent Expense: 800
Total Operating Expenses
Income from Operations
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Insurance Proceeds
Interest Expenses
Total Non-Operating Income
Net Income6,500
(1,400)
5,100
(400)
(860)
(1,260)
3,840
1,000
(750)
250
4,090
- Check the income statement of BizzBooz Pvt. Ltd. for the 2025 financial year, where they have generated net income of $4510 and gross profit of $6000.
Income Statement of BizzBooz Pvt. Ltd. for the year ending in 2025 (in $) Sales
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses
Selling Expenses
Advertising: (100)
Utilities: (300)
Freight Out: (400)
Depreciation: (50)
Salaries: (100)
Administrative Expenses
Supply Expense: (60)
Rent Expense: (800)
Insurance: (60)
Total Operating Expenses
Income from Operations
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Loss on Sale of Land
Insurance Proceeds
Interest Expenses
Total Non-Operating Income
Net Income7,000
(1,000)
6,000
(950)
(920)
(1,870)
4,130
(70)
850
(400)
380
4,510
- Here’s a detailed income statement of NexaSolve for the 2025 financial year, where they have generated net income of $24300 and gross profit of $32000.
Income Statement of NexaSolve for the year ending in 2025 (in $) Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses
Selling Expenses
Advertising Expenses: (500)
Payroll Taxes: (750)
Travel and Entertainment: (1,200)
Sales Commission: (500)
Supplies: (1,000)
Administrative Expenses
Supply Expense: (400)
Office Equipment: (2,000)
Rent Expense: (1,200)
Total Operating Expenses
Income from Operations
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Insurance Proceeds
Interest Expenses
Loss on Lawsuit
Total Non-Operating Income
Net Income
46,000
(14,000)
32,000
(3,950)
(3,600)
(7,550)
24,450
1,500
(750)
(900)
(150)
24,300
Single Step Vs Multi Step Income Statement

While a single step income statement is easy to prepare by deducting total expenses from net revenue, A multi-step income statement delivers more detailed insight into the firm’s true profitability.
Subsequently, there are several other differences that you can understand by referring to our table of single step vs multi step income statements below:
| Attribute | Single Step Income Statement | Multiple Step Income Statement |
| Definition | It is a simple income statement that deducts all expenses and losses incurred by the business from the net revenue to calculate net income. | This is a comprehensive financial report that has the separation of operating income from non-operating items before calculating net income. |
| Scope | Provides an overview of the profitability and financial performance of the business. | Delivers a complete insight into the financial health and performance of a firm. |
| Advantage | An easy-to-prepare income statement that requires less time and effort for calculation. | Assists in analysing how the profit was made by the business to improve operational efficiency. |
| Formula | Net Income = (Total Revenue & Profit) – (Total Expenses & Losses) | Net Income = Operating Income + (Non-operating Income – Non-operating Expenses) |
| Limitation | Lacks detailed insights into the sources of profit made by the firm. | A time-consuming process, as a multiple-step income statement reports multiple levels of profit. |
Pros and Cons of Multi-Step Income Statement
While a multiple step income statement provides a substantial and detailed financial report of net income, it is also a time-consuming and complex process.
However, you can opt for bookkeeping services and payroll services from a reliable firm that can assist you in gathering essential data for an accurate multi step income statement preparation.
Besides this, to understand the advantages and limitations, refer to the table below:
Who Uses a Multi-Step Income Statement?

Firms of each size utilise multi step income statements to gain meticulous details of their profits, along with other operating and non-operating revenues and expenses.
Here are the primary firms that use a multi step income statement:
- Large Businesses: Global firms and large-scale companies utilise effective preparation of a multi step income statement for better clarity and detailed insight into revenue and profits.
- Manufacturers: Since these income statements reveal meticulous profitability through gross profit after deducting COGS, retailers and manufacturers use them for income statements and cash flow statements.
- Small Business and Limited Companies: Since it is a more complex process that requires optimal knowledge, smaller firms use limited company accounting services for accurate and detailed preparation.
- Publicly Listed Companies: Publicly traded companies utilise multi step income statements to provide efficient financial reports to the public and institutional investors.
Conclusion
To understand easily, refer to multi step income statements as the meticulous financial report that firms develop to gather insights into their financial health, earnings, and profits.
Since it segregates operating income from non-operating revenue, losses, and expenses, businesses can identify profits generated from their fundamental business activities. Hence, students, businesses, or analysts can significantly benefit from multi-step income statements. For businesses seeking deeper profitability insights, the multi step income statement remains one of the most effective financial reporting tools.
- What Is a Multi Step Income Statement?
- Why Is a Multi Step Income Statement Important?
- Structure of a Multi-Step Income Statement
- Multi-Step Income Statement Format
- Example of a Multi-Step Income Statement
- Single Step Vs Multi Step Income Statement
- Pros and Cons of Multi-Step Income Statement
- Who Uses a Multi-Step Income Statement?
- Conclusion








