Certified payroll reporting can be described as the weekly reporting or payroll documents that are used to establish the payment of prevailing wages to workers on government projects, as mandated by law. It is applicable to government projects, whether it is federal, state, or local.
Contractors and subcontractors who work on the government-funded construction projects are bound to follow compliance, i.e., certified payroll reporting. It is a payroll report that records the number of straight hours worked, overtime compensation, total working hours, and other minute details so that the workers are classified properly and paid fairly.
The government takes certified payroll reports quite seriously under the Davis-Bacon Act, and failure to comply leads to penalties. This is similar to how annual accounting obligations such as year end accounts & CT returns services must be handled with precision and timeliness.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about government-certified payroll, the procedure, and the certified payroll forms that are utilized. Let’s get into it!
What is Certified Payroll?
Certified payroll is a record in which the wages given to the employees in government work or government-funded construction works are recorded. These records will ensure fair payroll processing. Employees obtain the prevailing wage and fringe benefits that they are entitled by law to receive within their job category and geographical area of work.
Payroll is certified, where the employer attests to a formal statement of compliance, which is legally binding, that:
- Payroll information is fully developed and correct.
- Workers are categorized correctly.
- The employees are being paid at or above the current wage rates.
- Overtime and fringe benefits are computed properly.
This is a certification accredited by law, and therefore, accuracy is very much needed. Similar attention to accuracy is required when outsourcing financial operations such as accounts payable services to ensure all vendor payments comply with reporting standards.
What Does Certified Payroll Reporting Mean?
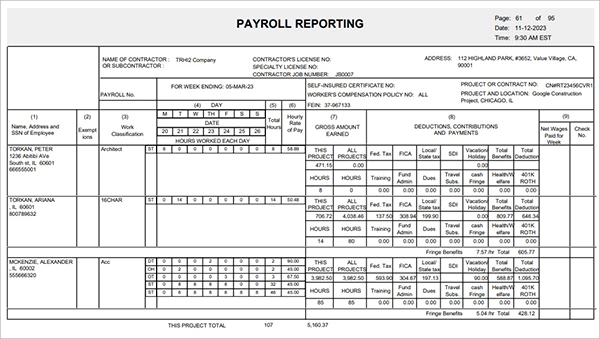
Certified payroll reporting refers to the systematic method of gathering payroll information, filling out the necessary forms, certifying the adherence, and reporting to the necessary federal, state, or local government.
Certified payroll reporting differs from ordinary payroll because:
- It’s submitted weekly.
- Needs the detailed wage and hour records.
- Has a statement of certification that is legally binding.
- Even where there is no work done in a given week, reports have to be made, usually under a no-work payroll.
Whether you’re preparing certified payroll reports or generating management accounts services for internal review, detailed records and consistency are vital.
Why Government Certified Payroll Reporting Matters?
Certified payroll reporting has various important uses in the construction and public contracting ecosystem.
- Protects Workers: Prevailing wage laws ensure that workers are not subjected to wage suppression and that they are well remunerated according to the local market rates and offered their payslips.
- Ensures Fair Competition: The wage requirements of all contractors who bid on government projects should be the same, and bid rigging by exploiting the wage structure should not take place. This ensures that they are not depending on some other financing sources, like a payroll card.
- Facilitates Government Supervision: Certified payroll reports give the agencies a clear-cut method of checking whether there is compliance and also of implementing labor legislation.
- Minimizes Legal and Financial Risk: Proper reporting will assist the contractors to evade audits, fines, lapsed payments, and disqualification.
Who and When Do We Need to Comply with Government Certified Payroll?
The reporting of government certified payroll is important when the construction project is federally funded, federally assisted, and regulated by a state or local prevailing wage system.
These are the primary types of projects that will require certified payroll:
- Highways and bridges.
- Universities and public schools.
- Government buildings.
- Sewer and water facilities.
- Projects in transit and transport.
As these are the major projects that need reporting, the following parties must carry out the submission process:
- Prime contractors
- Subcontractors of all tiers
- Labor-only subcontractors
Ultimately, it is the responsibility of the prime contractor to ensure that all the subcontractors make compliant payroll reports.
The Davis-Bacon Act and Certified Payroll Explanation
The federal certified payroll requirements are based on the Davis-Bacon Act (DBA). It is applicable in federally funded construction projects with a value of more than 2,000.
The requirement of the Davis-Bacon Act:
- Local prevailing practices are followed, and wages are paid.
- Fringe benefits should be included.
- Effective classification of workers.
- Proper reporting of overtime and compensation.
The US government, through the Department of Labor (DOL), values the prevailing wage rates depending on the geographical area and job type. According to the state and local rules, the contractors are bound to adhere to the federal laws. Comparable compliance attention is essential in areas like VAT return services where statutory deadlines and rates fluctuate.
What is a Certified Payroll Report, and How Does It Differ from a Regular Payroll Report?
A certified payroll report (CPR) refers to the formal weekly report that records payroll compliance with regard to covered projects.
Every report gives a descriptive picture of:
- Who worked?
- What work did they perform?
- How many hours did they work?
- How much they were paid.
- What deductions were taken?
However, most importantly, it contains a signed certification that it meets the relevant labor laws. This distinction mirrors the difference between general oversight like accounting services and compliance-specific reporting such as certified payroll obligations.
Certified payroll and regular payroll reports may appear to be the same, however, their mission and demands are very different.
| Certified Payroll Report | Regular Payroll Report |
| Applicable to public work projects only. | It carries general business operations. |
| Should comply with the prevailing wage legislation. | Adheres to the common tax and labor legislation. |
| Weekly report to government agencies. | No filing in the government is needed. |
| Done by the certified lawyer. | Wage rates are set by the employer. |
Certified Payroll Forms: Overview
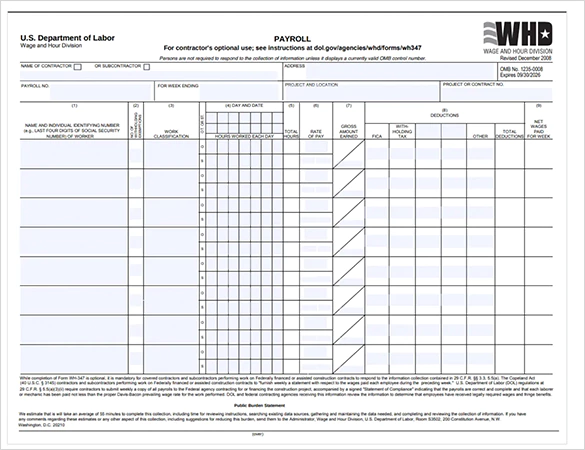
Certified payroll reporting forms do not have a standardized format. Although the most commonly accepted one is the Form WH-347 in the US. Department of Labor, contractors in areas of the work within a public work may have to complete different types of certified payroll forms based on the source of funds and regulations.
These are the following certified payroll reporting form in federal, state, and local projects:
Federal Certified Payroll Form (WH-347)
It is the standard certified payroll reporting form that is issued by the US Department of Labor and is mainly utilized with projects that fall under the Davis-Bacon and Related Acts. It takes a record of the employee wages, the hours worked, the job classification, fringe benefits, deductions, and a statement of compliance, which is mandatory.
State-Specific Payroll Forms
Lots of states have prevailing wage laws that require contractors to file certified payroll reports on state-provided forms or portals. These forms can seek extra information, work-specific pay rates, or benefits other than those required by the federal government.
Local or Municipal Certified Payroll Forms
Cities, counties, and local governments may adopt their own certified payroll reporting formats in regard to projects funded by the municipality in the public works. These regional versions tend to replicate WH-347, but they have additional domains of local wage ordinances.
How to Fill Out a Certified Payroll Form?
A certified payroll form has to be filled with accuracy, uniformity, and understanding of current wage regulations. Minor mistakes are enough to result in rejection of the submission or compliance audit.
- Write the name of all employers, project information, the name of the legal business, the address, and the name of the contractor, subcontractor, and payroll number.
- Next, name all covered employees who worked within the reporting week, the names should be correct, and the numbers should be properly recorded to prevent discrepancies in cases of audits.
- Give the right job classification to every worker, whether it is electrician, carpenter, laborer, or equipment operator, as wage rates are dependent on the classification and locality.
- Record hours worked daily and weekly so that there is a distinction between straight-time hours and overtime hours. Just as accurate accounts receivable services outsourcing helps businesses capture every dollar, accurate payroll ensures every worker receives what they are due.
- Give proper fringe benefits and appropriate hourly rates, and ensure that the summation of cash wages plus the fringe benefits satisfies or exceeds the relevant prevailing wage determination.
- Take gross wages, deductions, and net pay, and list all deductions, including federal taxes or other authorized deductions, and ensure that net wages are identical to payroll records.
- Sign the statement of compliance, and this certifies the information that is given to be true and that all workers were paid as per the current labor laws. Similar to how professionals may use tax outsourcing support for complex reporting.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with Certified Payroll
Failure to adhere to certified payroll may have severe financial, legal, and reputational implications for contractors and subcontractors. The government agencies punish for certified payroll violations under the violation of labor law.
The possible penalties are:
- Civil penalties and monetary fines, which may add up quite fast, should cut across several employees or reporting periods.
- Back payments of wages are given to the employees who were affected, along with added benefits.
- Withholding of contract funds until the pending settlement of certified payroll concerns.
- Publicity of violations can destroy the reputation of the company and diminish the chances of future work.
- Contractors can also be criminally charged in instances involving willful falsification or deliberate misrepresentation.
Wrapping Up!
Certified payroll reporting is a complicated yet obligatory rule for contractors engaged in government-funded and government work. Since certified payroll forms are quite complex to understand, and weekly report filing and compliance with the strict standards are required, the process is not an easy one and requires dense attention to detail and regular execution.
Proper certified payroll management is not only a way to ensure the workers and to fulfill legal requirements, but also to enhance the credibility and the success of contractors in the field of public contracts.
- What is Certified Payroll?
- What Does Certified Payroll Reporting Mean?
- Why Government Certified Payroll Reporting Matters?
- Who and When Do We Need to Comply with Government Certified Payroll?
- The Davis-Bacon Act and Certified Payroll Explanation
- What is a Certified Payroll Report, and How Does It Differ from a Regular Payroll Report?
- Certified Payroll Forms: Overview
- How to Fill Out a Certified Payroll Form?
- Penalties for Non-Compliance with Certified Payroll
- Wrapping Up!










